Heart Failure: Causes, Treatments, and What You Need to Know
When someone says heart failure, a condition where the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Also known as congestive heart failure, it's not a sudden stop—it's a slow decline in function that builds over time. Many people think heart failure means a heart attack, but it’s different. It’s more like a worn-out engine struggling to keep up. You might feel tired, short of breath, or notice swelling in your legs. These aren’t just signs of aging—they’re signals your heart is working too hard.
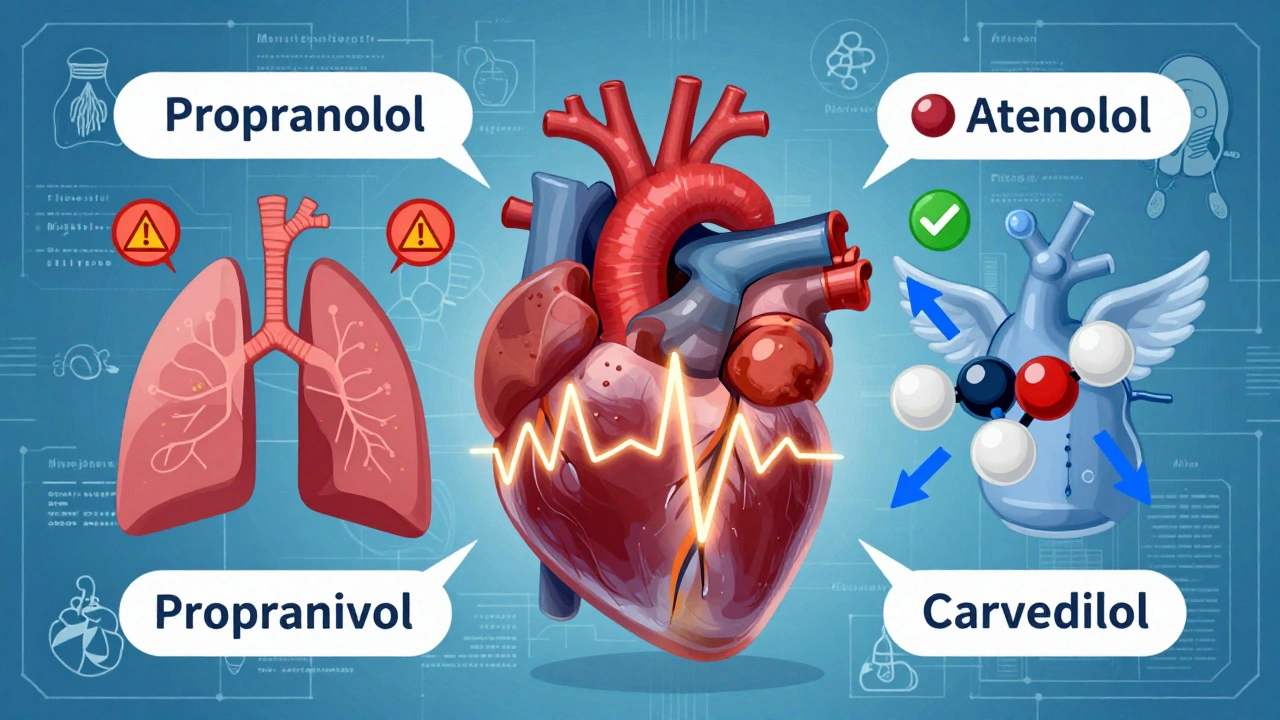
What causes it? High blood pressure, coronary artery disease, or past heart attacks are the big ones. But other things matter too—like long-term use of certain meds. For example, eplerenone, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure helps the body get rid of extra fluid and lowers strain on the heart. But it comes with a trade-off: long-term use can affect bone density, raising the risk of osteoporosis, a condition where bones become weak and brittle. That’s why monitoring isn’t just about your heart—it’s about your whole body.
Diagnosis matters just as much as treatment. Two common tools used to see what’s going on inside your heart are cardiac MRI, a detailed imaging test that shows heart structure and tissue damage and echocardiography, an ultrasound that shows how well your heart pumps and valves work. One gives you a high-res picture; the other gives you real-time motion. Doctors pick based on what they’re looking for—scarring, valve leaks, or pumping strength. And if you’re on blood thinners, medications that prevent clots but require careful management to avoid bleeding, timing and reversal options become critical. Drugs like idarucizumab can undo their effect fast in an emergency—but only if you know they’re in your system.
Heart failure isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition. Your treatment plan depends on your age, other health issues, and even how you take your meds. Some people do better taking blood pressure pills at night. Others need to watch protein intake if they’re on Parkinson’s meds. And if you’re on multiple drugs, interactions can sneak up on you—even with generics. That’s why reading medication guides and knowing your exact meds matters more than ever.
What you’ll find below isn’t just theory. It’s real advice from people who’ve been there: how to spot warning signs before they turn dangerous, what tests actually tell you, and how to talk to your doctor about side effects you’re too scared to mention. From how eplerenone affects your bones to why a cardiac MRI might be worth the wait, these posts cut through the noise. No fluff. No jargon. Just what you need to manage heart failure—not just survive it, but live with it.