Beta-Blockers: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your heart beats too fast or too hard, beta-blockers, a class of medications that slow down the heart and reduce blood pressure by blocking adrenaline. Also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, they’re one of the most prescribed drug types for heart-related conditions. You might be on them if you have high blood pressure, angina, irregular heartbeat, or even anxiety. They don’t cure anything—they just help your body handle stress better by calming down the nervous system’s fight-or-flight response.
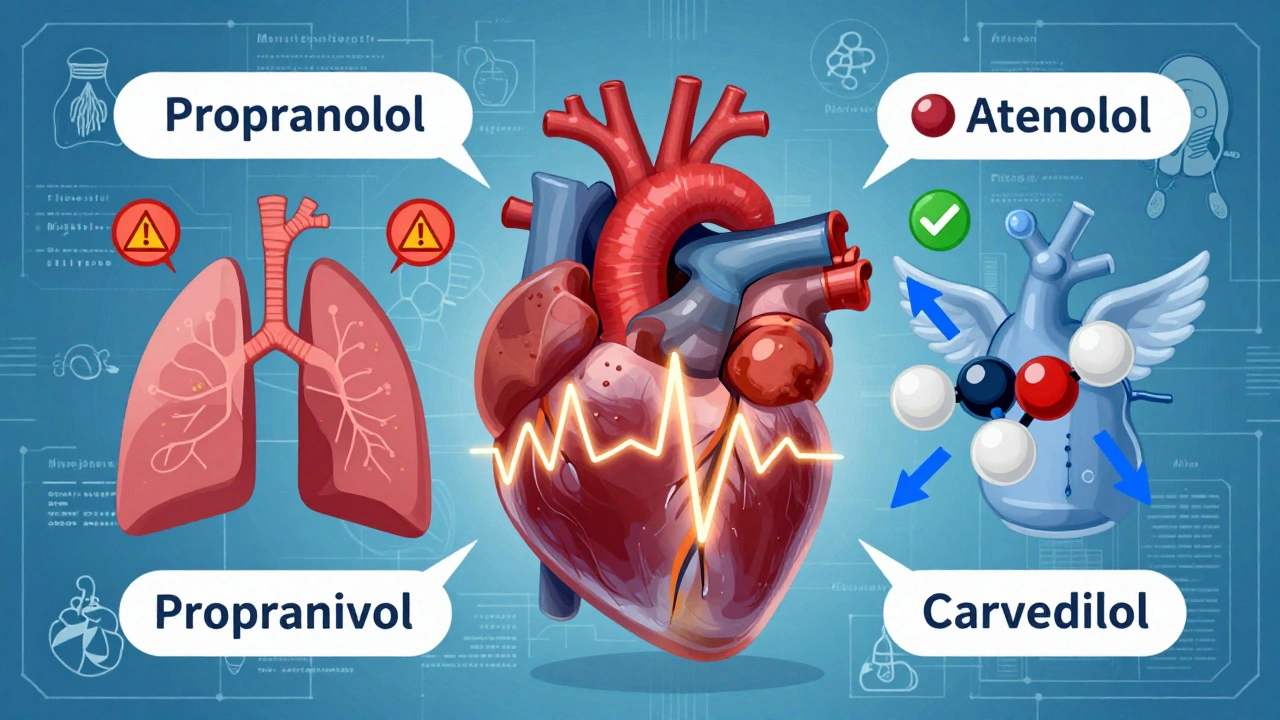
These drugs work by blocking beta receptors in your heart and blood vessels. That means less adrenaline can bind and make your heart race or your arteries tighten. Common types include metoprolol, a selective beta-blocker often used for heart attacks and high blood pressure, atenolol, a longer-acting option that’s gentle on the lungs, and propranolol, a non-selective version that can also help with tremors and migraines. Each has its own use case, and your doctor picks based on your health, other meds, and side effect risks.
They’re not without trade-offs. Fatigue, cold hands, dizziness, and slow heart rate are common. Some people get depressed or have trouble sleeping. And if you have asthma or diabetes, beta-blockers can make things trickier—they can hide low blood sugar symptoms or tighten airways. That’s why you can’t just start or stop them on your own. Tapering off too fast can trigger chest pain or even a heart attack. Also, they interact with other meds: calcium channel blockers, certain antidepressants, and even some over-the-counter cold pills can turn dangerous when mixed.
What’s surprising is how often people take them without knowing why. Many assume they’re just for blood pressure, but they’re also used after heart attacks to prevent future ones, for migraine prevention, and even for performance anxiety in musicians or public speakers. The science behind them is solid, but the real-world use? It’s messy. Some patients feel better right away. Others feel like they’re walking through mud. And because they’re cheap and generic, they’re often the default choice—even when newer drugs might suit you better.
That’s why understanding your specific version matters. If you’re on beta-blockers, you need to know how they affect your daily life: when to take them, what to avoid, how to spot warning signs, and whether your symptoms are from the drug or your condition. The posts below cover exactly that—how to read your medication guide, what interactions to watch for, how timing affects side effects, and how to talk to your pharmacist about safer alternatives. You’ll find real advice from people who’ve been there, not just textbook definitions. No fluff. Just what you need to stay safe and in control.