Glyset (Miglitol) vs Alternatives: A Practical Comparison
A detailed comparison of Glyset (miglitol) with other diabetes meds, covering pros, cons, costs, side effects, and how to pick the best alternative for your needs.
When dealing with type 2 diabetes medication, any drug prescribed to lower blood sugar in adults diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Also called T2DM meds, it is essential for preventing heart disease, kidney damage, and vision loss. Understanding how these medicines work helps you pick the right plan, and that’s why type 2 diabetes medication knowledge matters.
One of the most common oral options is Metformin, a first‑line drug that cuts liver glucose production and boosts insulin sensitivity. For people who need stronger glucose control, GLP‑1 agonists, injectable agents that stimulate insulin release after meals and often promote weight loss are a solid choice. SGLT2 inhibitors, pills that block kidney reabsorption of glucose, helping excess sugar leave the body through urine add another layer of protection, especially for patients with heart or kidney concerns. Finally, Insulin therapy, injectable hormone replacement for those whose bodies no longer produce enough insulin remains the backbone for advanced disease. These four groups together illustrate that type 2 diabetes medication includes oral agents and injectable therapies, each targeting a different physiological pathway.
Beyond the drugs themselves, effective management hinges on regular blood‑sugar monitoring. Glucometers give real‑time feedback, letting you see how meals, activity, or a new prescription affect your numbers. Pairing monitoring with medication choices creates a feedback loop: if Metformin alone isn’t keeping fasting glucose under control, your doctor might add an SGLT2 inhibitor or switch to a GLP‑1 agonist. Side‑effect profiles also guide decisions—Metformin can cause gastrointestinal upset, GLP‑1 agonists may trigger nausea, while SGLT2 inhibitors increase the risk of urinary tract infections. Knowing these trade‑offs helps you weigh benefits against potential drawbacks before committing to a regimen.
Patient‑specific factors shape which medication fits best. Kidney function, for example, limits high‑dose Metformin and some SGLT2 inhibitors; cardiovascular history often pushes clinicians toward GLP‑1 agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors that have proven heart‑protective benefits. Weight considerations matter too—many people appreciate the modest weight loss seen with GLP‑1 therapies, whereas insulin can lead to weight gain. Cost and insurance coverage are practical realities; generic Metformin is usually inexpensive, while newer GLP‑1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors may require prior authorization. By matching drug attributes—mechanism of action, side‑effects, dosing frequency—to your health profile, you can build a personalized plan that feels sustainable.
All of these pieces—drug classes, monitoring tools, patient characteristics—combine to form a comprehensive picture of type 2 diabetes treatment. Below, you’ll find articles that dive deeper into each medication, compare their pros and cons, and offer step‑by‑step guides for buying affordable generics safely. Whether you’re new to T2DM meds or looking to fine‑tune an existing regimen, the collection ahead equips you with the facts you need to make informed choices.
A detailed comparison of Glyset (miglitol) with other diabetes meds, covering pros, cons, costs, side effects, and how to pick the best alternative for your needs.
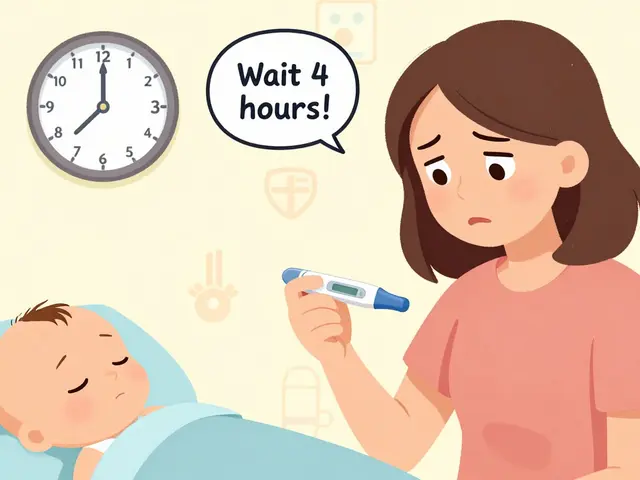

Learn the right time to give fever reducers after your child's vaccines. Discover why waiting 4 hours matters, which vaccines cause the most fever, and when to use medicine safely.
Learn how to safely buy cheap generic Neurontin online in Australia, verify legitimate pharmacies, compare prices, and avoid common scams.

Pancreatic cancer, often detected too late, poses higher risks as we age. This article explores why aging increases vulnerability to this aggressive cancer, highlighting crucial warning signs and the importance of early detection. Find practical tips for reducing risks and insights into the latest research. The link between age and pancreatic cancer isn't just a number game—it involves lifestyle and genetic factors, which we'll unpack.
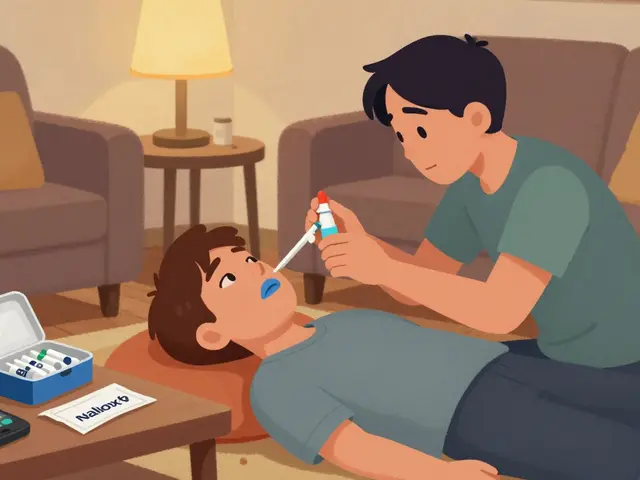

Learn how naloxone reverses opioid overdoses, how to recognize the signs, where to get it for free, and how to store it safely. A practical guide for families, friends, and community members.

I recently came across the Bishop's Weed dietary supplement and I must say, it has truly changed my life! Not only has it helped improve my digestion, but it has also given my immune system a much-needed boost. I've noticed a significant increase in my energy levels and overall well-being since I started incorporating it into my daily routine. I highly recommend giving Bishop's Weed a try if you're looking to experience its incredible benefits for yourself. Trust me, you won't be disappointed!
