Nebivolol: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
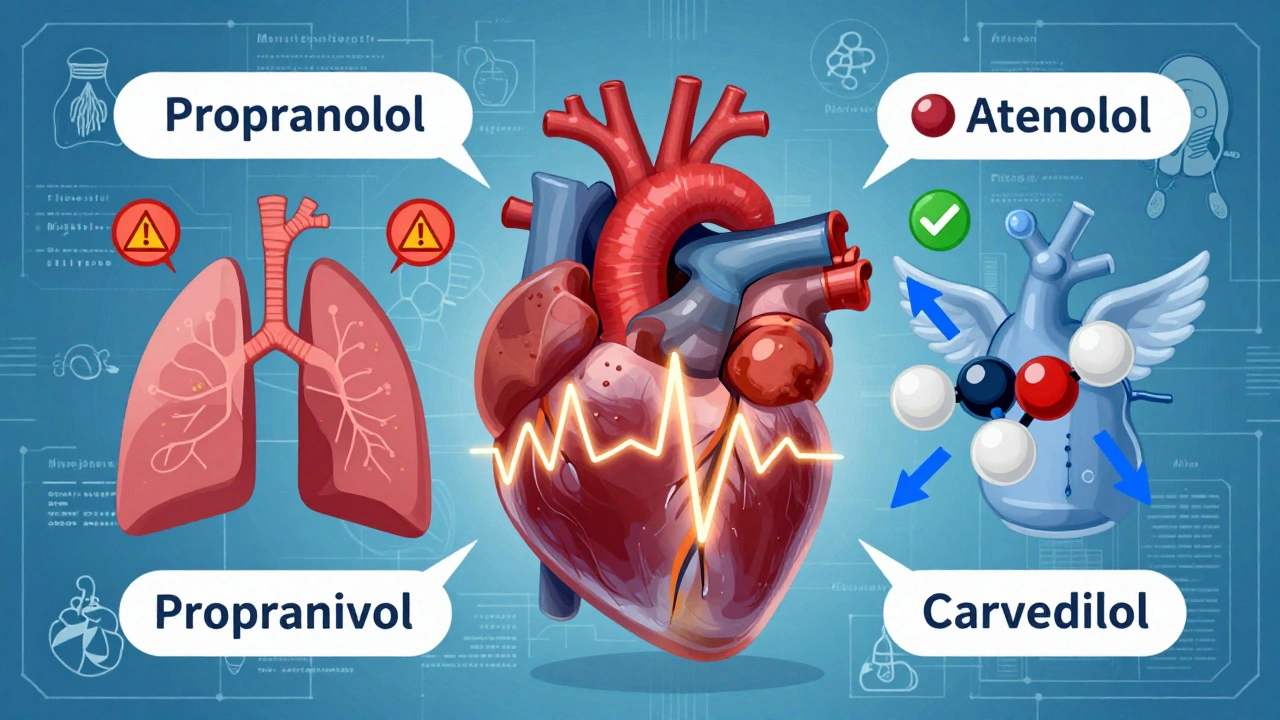
When you're prescribed nebivolol, a selective beta-1 blocker used to lower blood pressure by slowing the heart and relaxing blood vessels. Also known as Bystolic, it's one of the newer beta blockers on the market, designed to work differently than older ones like metoprolol or atenolol. Unlike some other heart meds, nebivolol doesn’t just slow your heart—it also helps widen your arteries by boosting nitric oxide, which improves blood flow. That’s why many people notice fewer side effects like fatigue or cold hands compared to older drugs.
This makes nebivolol, a cardiovascular drug often chosen for patients who need gentle, long-term blood pressure control a good fit for older adults or those with asthma or diabetes, where other beta blockers might cause trouble. It’s also used in people with heart failure, though not as a first-line choice. The key thing to remember: nebivolol, a once-daily antihypertensive that takes a few weeks to reach full effect isn’t a quick fix. You won’t feel it working, but your numbers will drop over time. And unlike some meds, it doesn’t usually cause weight gain or make you sleepy during the day.
People on nebivolol often wonder about timing—should they take it in the morning or at night? Research suggests taking it at bedtime may reduce morning blood pressure spikes and lower the risk of dizziness when standing up. But if you’re also on other heart meds like diuretics or ACE inhibitors, your doctor might adjust the schedule to avoid interactions. And while nebivolol is generally safe, it can interact with certain antidepressants, calcium channel blockers, or even over-the-counter cold medicines. Always check with your pharmacist before adding anything new.
You’ll also find that many patients on nebivolol are monitored for heart rate and kidney function. It’s not just about lowering numbers—it’s about keeping your body balanced. If your pulse drops below 50 beats per minute or you feel unusually tired, that’s a signal to talk to your provider. Some people need blood tests to check electrolytes, especially if they’re also taking diuretics.
What you won’t find in most drug ads is how nebivolol fits into real life. It’s not just a pill—it’s part of a bigger picture. People who take it often combine it with diet changes, walking, or stress management. And because it’s not a cure, you’re likely on it for years. That’s why understanding how it works, what to expect, and how to spot problems matters more than the brand name on the bottle.
The posts below cover exactly these kinds of real-world concerns: how to safely split pills to save money, when to take blood pressure meds for fewer side effects, what to do if you miss a dose, and how to avoid dangerous interactions with other drugs. You’ll also find guides on reading medication labels, reporting side effects, and understanding why some generics behave differently than others. This isn’t theory—it’s what people actually deal with when they’re managing high blood pressure long-term. Whether you’re new to nebivolol or have been on it for years, there’s something here that will help you take better control.