Skin Barrier Health Calculator
This tool estimates how stress is affecting your skin barrier and provides personalized recommendations based on your inputs.
Assess Your Current Situation
Your Skin Barrier Health Report
If you’re battling chapped skin, understanding stress’s role is key.
Key Takeaways
- Stress spikes cortisol, which weakens the skin barrier and speeds up moisture loss.
- Weather, low humidity, and frequent hand washing are common triggers for chapped skin.
- Barrier‑repair moisturizers with ceramides or hyaluronic acid restore lost lipids and attract water.
- Mind‑body techniques like deep breathing and short walks lower stress hormones within minutes.
- Persistent cracking, bleeding, or infection warrants a dermatology visit.
What Is Chapped Skin?
Chapped skin is a condition where the outer layer of the skin becomes dry, cracked, and painful. It most often shows up on hands, lips, and any area exposed to harsh winds or frequent washing.
The problem starts when the skin’s natural moisture barrier can’t hold water. When that barrier breaks down, you feel tightness, see visible lines, and the skin may even bleed.
How Stress Messes With Your Skin Barrier
Stress is a psychological response that triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that helps the body cope with short‑term threats. While useful in emergencies, chronic cortisol elevation has a dark side for skin health.
Research from a 2023 dermatology study shows that sustained high cortisol reduces the production of ceramides, key lipids that seal the skin barrier. Less ceramide means more water evaporates, and the skin becomes prone to cracking.
Moreover, cortisol promotes inflammation. Inflamed skin swells, its pH shifts, and the natural microbiome gets disrupted, all of which accelerate the chapping cycle.
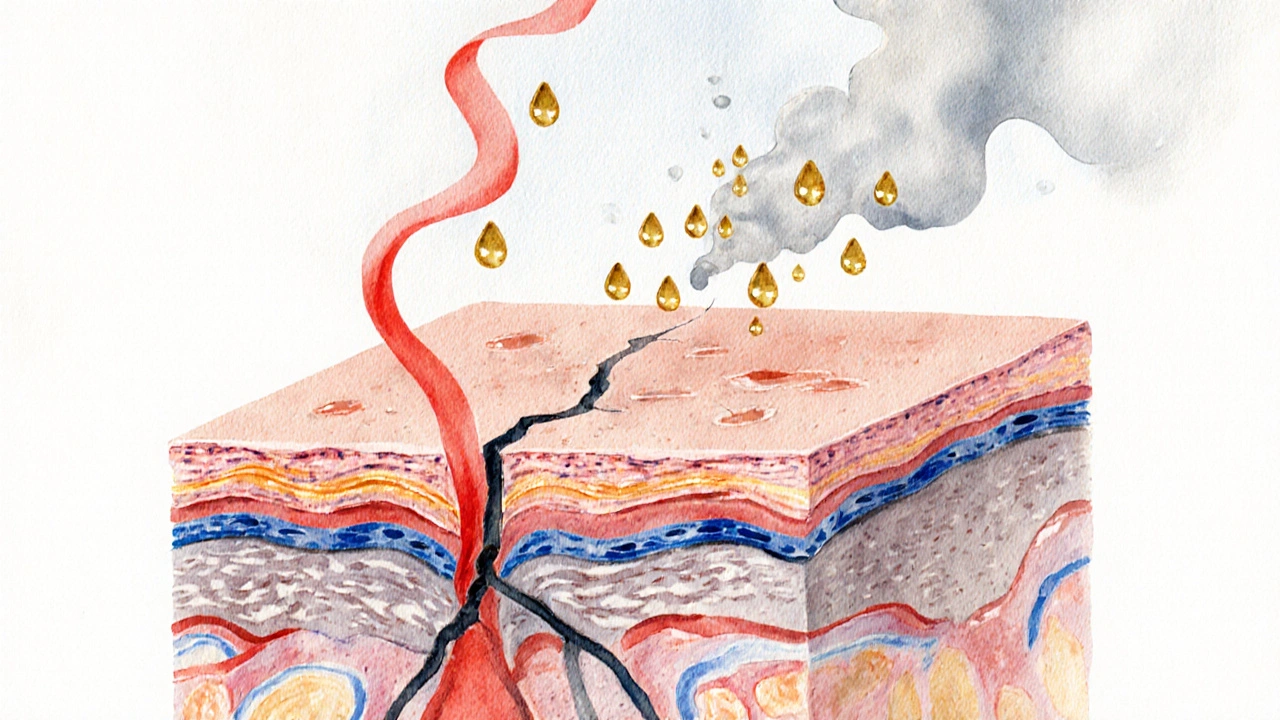
Common Triggers That Compound the Stress Effect
- Low indoor humidity during winter or air‑conditioned environments.
- Frequent hand washing, especially with hot water and harsh soaps.
- Exposure to wind, cold, or sun without protection.
- Underlying skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
- Poor nutrition - low omega‑3 intake and dehydration.
When any of these factors combine with a stressed mindset, the skin barrier’s repair mechanisms can’t keep up, leaving you with stubborn cracks.
Immediate Relief: Quick Fixes for a Bad Day
- Pat your skin dry - don’t rub. Rubbing strips away the thin protective film that’s left.
- Apply a thin layer of a barrier‑repair moisturizer within three minutes of washing. The faster you seal in moisture, the better.
- Cover extreme cracks with a breathable ointment (e.g., petroleum jelly) for a few hours or overnight.
- Drink a glass of water and snack on a handful of almonds for a quick omega‑3 boost.
- Take a five‑minute deep‑breathing pause: inhale for 4 seconds, hold 7, exhale 8. This simple technique can lower cortisol within minutes.
Long‑Term Strategies: Repairing the Barrier and Reducing Stress
Consistent care beats occasional patches. Below is a comparison of the most effective topical formulas.
| Type | Occlusiveness | Best For | Key Ingredients | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ointment | Very high | Severe cracks, night‑time repair | Petrolatum, mineral oil | Locks in moisture for hours | Greasy feel, not ideal under makeup |
| Cream | Medium‑high | Daily use, mild‑to‑moderate dryness | Ceramides, hyaluronic acid, glycerin | Balanced feel, fast absorption | May need re‑application in very dry climates |
| Lotion | Low‑medium | Seasonal dryness, post‑shower | Water, light oils, aloe | Lightweight, non‑greasy | Less protective in extreme cold |
For most people, a **cream** with ceramides and hyaluronic acid hits the sweet spot. Ceramides rebuild the lipid matrix, while hyaluronic acid draws water from the deeper layers.

Nutrition and Lifestyle Tweaks
Eating skin‑friendly foods fuels the barrier from the inside out.
- Omega‑3 fatty acids - found in salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds - reduce inflammation and support lipid production.
- VitaminE - almonds, sunflower seeds - acts as an antioxidant that protects cell membranes.
- Water - aim for at least 2liters daily, more if active or in hot climates.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol, both of which can dehydrate skin.
Combine these diet changes with a regular sleep schedule; 7‑9hours per night helps regulate cortisol rhythms.
Mind‑Body Practices to Lower Cortisol
Stress management isn’t a luxury; it’s part of skin therapy.
| Technique | Time Needed | Effect on Cortisol |
|---|---|---|
| Box breathing (4‑4‑4‑4) | 2minutes | ↓ up to 30% |
| Progressive muscle relaxation | 5minutes | ↓ up to 25% |
| Short walk in nature | 10minutes | ↓ up to 20% |
| Journaling gratitude | 3minutes | ↓ up to 15% |
Pick one that fits your routine and practice it daily. Even a brief pause can reset the stress response and give your skin a chance to repair.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you notice any of these signs, schedule an appointment with a dermatologist:
- Cracks that bleed or ooze.
- Persistent redness or swelling despite home care.
- Signs of infection - pus, warmth, fever.
- Rapid spreading across large areas.
A professional may prescribe a mild topical steroid, barrier‑repair ointment, or recommend phototherapy for underlying conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of chapped skin?
The skin loses moisture when the barrier is stripped by low humidity, frequent washing, harsh soaps, wind, or extreme temperatures. Stress‑induced cortisol also reduces lipid production, making the barrier even weaker.
How does stress specifically worsen dry skin?
Stress raises cortisol, which cuts down ceramide synthesis and promotes inflammation. Less ceramide means faster water loss, and inflammation makes the skin more sensitive and prone to cracking.
Can drinking more water prevent chapped skin?
Hydration helps maintain overall skin health, but the outermost layer still relies on external moisturizers. Combine adequate water intake with barrier‑repair creams for best results.
Are there any ingredients I should avoid?
Fragrances, alcohol, and harsh preservatives can strip natural lipids. Opt for fragrance‑free, hypoallergenic formulas that list ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or glycerin as key ingredients.
When is it time to see a dermatologist?
If cracks bleed, become infected, or don’t improve after a week of diligent care, get professional help. Persistent redness, swelling, or widespread chapping may signal an underlying skin condition that needs prescription treatment.
By tackling both the external factors (moisture loss, harsh products) and the internal ones (stress, diet), you can break the cycle of chapped skin and enjoy smoother, healthier skin every day.










16 Comments
Stress makes your skin crack like old parchment, fix it! 😤
While stress does spike cortisol, remember hydration and barrier‑repair creams are your first line of defense; a quick moisturizer after washing can seal in moisture effectively.
Think of your skin like a fortress; when cortisol storms the walls, you need ceramide‑rich reinforcements and a breath of fresh air to keep the moat from drying out.
Adding a splash of omega‑3s and a short walk can turn the tide.
Research indicates that chronic cortisol elevation reduces ceramide synthesis which compromises the stratum corneum and accelerates transepidermal water loss
First, acknowledge that stress is a real physiological trigger that can undermine the skin’s natural barrier; you’re not imagining the cracks.
Second, prioritize a barrier‑repair moisturizer that contains ceramides and hyaluronic acid, applying it within three minutes of washing to lock in hydration.
Third, incorporate a simple breathing exercise like box breathing for two minutes each morning; studies show it can lower cortisol by up to 30 %.
Fourth, stay hydrated by drinking at least two liters of water daily, and consider adding a handful of walnuts for omega‑3 fatty acids.
Fifth, protect your hands with gloves when doing chores that involve hot water or harsh detergents.
Sixth, use a humidifier in dry indoor environments to keep humidity above 40 %.
Seventh, avoid products with high alcohol or fragrance content, as they strip the lipid matrix further.
Eighth, if you notice persistent redness or bleeding, schedule a dermatologist visit promptly.
Ninth, sleep 7‑9 hours per night to help regulate cortisol rhythms.
Tenth, limit caffeine and alcohol intake, both of which can dehydrate the skin.
Eleventh, consider a short nature walk during lunch to give your nervous system a reset.
Twelfth, keep a small tube of ointment in your bag for emergency spot‑treating deep cracks.
Thirteenth, maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins E and C to support antioxidant defenses.
Fourteenth, be consistent – daily application of a good cream beats occasional heavy ointments.
Finally, remember that stress management and skin care go hand‑in‑hand; tackling both will break the cycle of chapped skin.
All that science, but if you skip the moisturizer, you’re just digging your own trench.
Grab a tube of ceramide cream, slap it on after every wash, and watch the cracks start to seal; consistency beats occasional heroics.
They don’t want you to know that the air‑conditioner fuels dryness – open a window! 🌬️
Oh sure, “just drink water” solves everything, but without a proper occlusive layer your skin will still scream for help; the real fix is a barrier‑repair cream plus a stress‑busting habit.
i think a humidifier at your desk can really help keep the skin from cracking.
Has anyone tried swapping their regular soap for a sulfate‑free version? I noticed my hands felt less tight and the cracks seemed to close faster.
Stop waiting for the perfect day – start the skin routine now and feel the boost!
Everyone talks about cortisol but forgets the real enemy is the cheap hand sanitizer that strips lipids.
One might consider that a nuanced approach to stress reduction, such as mindfulness meditation, complements dermal therapy elegantly.
Remember, small daily steps-like a brief walk and a moisturiser-add up to big improvements over weeks.
In summation, the integration of barrier fortification and cortisol mitigation constitutes a comprehensive strategy for combating chapped integument.