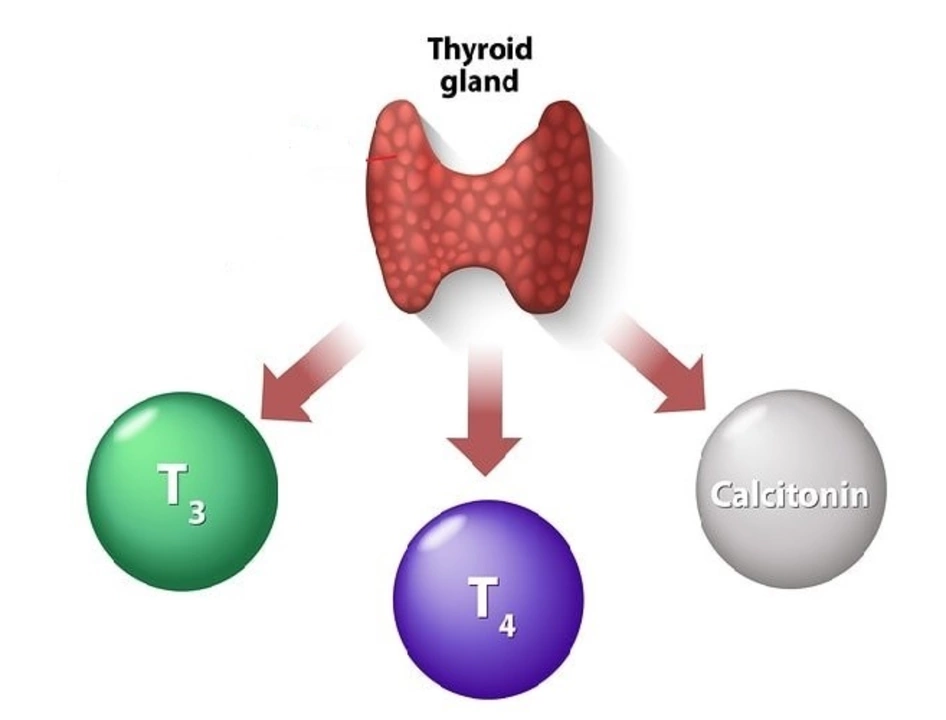
Understanding the Roles of Calcitonin and Vitamin D
Calcitonin and vitamin D are two essential hormones that play significant roles in maintaining our body's overall health. Calcitonin, produced by the thyroid gland, helps regulate calcium levels in our blood, while vitamin D, synthesized in our skin from sunlight exposure, aids in calcium absorption and bone health. In this section, we will delve into the individual functions of these hormones and their interplay in sustaining a healthy body.
Calcitonin is primarily responsible for preventing excessive calcium levels in our bloodstream. When calcium levels rise, the thyroid gland releases calcitonin, which then inhibits the release of calcium from our bones, decreases the absorption of calcium from our intestines, and increases the excretion of calcium through our kidneys. This mechanism helps maintain a balanced calcium concentration in our blood, which is crucial for various body functions such as nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and blood clotting.
Vitamin D, on the other hand, promotes the absorption of calcium from our diet and supports bone growth and remodeling. By facilitating the uptake of calcium in our intestines and regulating its deposition in our bones, vitamin D ensures that our body has adequate levels of this essential mineral to carry out its many functions. Furthermore, vitamin D also plays a role in modulating our immune system and reducing inflammation.
How Calcitonin and Vitamin D Work Together in Bone Health
Both calcitonin and vitamin D have significant impacts on our bone health, and their combined effects on calcium regulation are crucial in maintaining strong and healthy bones. While vitamin D promotes calcium absorption and bone growth, calcitonin helps prevent excessive calcium levels and bone resorption, a process where calcium is released from our bones into the bloodstream.
When our body requires more calcium, vitamin D enhances the absorption of this mineral in the intestines, and calcitonin production decreases, allowing for more calcium to be released from our bones. Conversely, when calcium levels are too high, calcitonin production increases, and the activity of vitamin D is reduced, preventing further calcium absorption and promoting its excretion. This delicate balance between calcitonin and vitamin D is essential in maintaining optimal bone health and preventing conditions such as osteoporosis and hypercalcemia.
Calcitonin and Vitamin D Deficiencies and their Effects on Health
Imbalances in the levels of calcitonin and vitamin D can lead to various health issues. A deficiency in calcitonin can result in hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by abnormally high calcium levels in the blood. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, nausea, kidney stones, and even abnormal heart rhythms. In severe cases, it can lead to kidney failure or coma.
Vitamin D deficiency, on the other hand, impairs calcium absorption and can cause conditions such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Both of these disorders involve the softening and weakening of bones, making them prone to fractures and deformities. Additionally, low levels of vitamin D have also been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer.
Boosting Calcitonin and Vitamin D Levels for Better Health
Given the importance of calcitonin and vitamin D in maintaining our body's overall health, it is essential to ensure that we have adequate levels of these hormones. To boost calcitonin levels, it is crucial to maintain a balanced diet that includes foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals. Additionally, certain medications can help regulate calcium levels if they are too high or too low.
For optimal vitamin D levels, it is necessary to have sufficient exposure to sunlight, as our skin synthesizes this hormone when exposed to UVB rays. However, excessive sun exposure carries risks, such as skin cancer, so it is crucial to balance sun exposure with sun protection measures. Vitamin D can also be obtained through dietary sources, such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements, if necessary. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate intake of vitamin D for your individual needs.
Conclusion: The Vital Connection Between Calcitonin and Vitamin D
In summary, calcitonin and vitamin D play vital roles in maintaining our body's calcium balance and bone health. By working together, these hormones ensure that our body has the necessary calcium levels to support various physiological functions, while also preventing excessive calcium concentrations that can be detrimental to our health. Ensuring that we have adequate levels of both calcitonin and vitamin D is essential for maintaining our overall well-being and preventing various health issues. By adopting a balanced diet, getting enough sunlight exposure, and consulting with healthcare professionals, we can optimize our calcitonin and vitamin D levels and enjoy better health.











9 Comments
Wow, this is such a nuanced topic-I’ve always thought of vitamin D as just the "sunshine vitamin," but the way calcitonin acts as a silent regulator, like a calm referee in a high-stakes game of calcium tug-of-war, is mind-blowing.
It’s not just about bones; it’s about rhythm, balance, harmony-like the way monsoon rains and dry seasons coexist in India, each serving a purpose.
And yet, we treat these hormones like on/off switches, when they’re more like ocean tides-subtle, cyclical, deeply connected to environment, culture, even stress.
I’ve seen elderly relatives in Delhi take calcium supplements like candy, never realizing that without vitamin D, it’s just expensive gravel passing through their system.
And calcitonin? Most people don’t even know it exists. It’s the quiet guardian, the unsung hero-like the village elder who knows when to speak and when to let silence do the work.
We need more public health narratives that honor this interplay-not just pills and prescriptions, but wisdom.
Maybe we should teach this in schools, not as biochemistry, but as philosophy of balance.
India’s traditional diets-milk with turmeric, fermented foods, sunlight at dawn-weren’t accidents. They were ancient protocols for hormonal harmony.
Modern medicine loves to isolate, quantify, patent-but nature works in whispers, not loudspeakers.
Let’s not lose the poetry in the physiology.
This article is pure woke science nonsense vitamin D is the only thing that matters calcitonin is a relic of outdated endocrinology and if you think your bones need help from some thyroid hormone you're just weak and lazy
Billy Tiger’s comment is exactly why Western medicine is failing us. You can’t reduce human biology to a single hormone and call it a day. Calcitonin isn’t a relic-it’s a regulator. And if you think vitamin D alone fixes everything, you’ve never seen someone with osteoporosis who’s been taking 5000 IU daily for a decade and still breaks a hip sneezing.
I appreciate the depth here. In my village in Bihar, elders used to say, 'Sunlight for bones, milk for strength, rest for balance.' They didn’t know the names calcitonin or vitamin D, but they knew the rhythm. Maybe science is just catching up to what tradition already knew.
The fact that this post even needs to explain calcitonin’s role suggests a fundamental failure in medical education. Anyone who’s taken a basic physiology course knows this. If you’re reading this and surprised, you shouldn’t be self-medicating with supplements-you should be in a classroom.
This is such a thoughtful breakdown-thank you for writing it.
I’ve been working with older patients for years, and I’ve seen how vitamin D deficiency slips under the radar because the symptoms are so vague-fatigue, aches, low mood-and people just chalk it up to ‘getting older.’
But when you check levels and supplement properly? Their energy comes back. Their balance improves. They stop falling.
And calcitonin? Honestly, most doctors don’t test for it, and honestly? They probably shouldn’t-unless someone’s got a thyroid tumor or severe hypercalcemia.
But understanding the relationship? That’s where the real insight lies.
It’s not about which one is ‘more important.’ It’s about how they dance together.
Like two musicians in a jazz trio-vitamin D plays the bassline, calcitonin is the drummer keeping the tempo steady, and the body? That’s the melody.
Let’s stop treating hormones like villains or heroes. They’re just part of the song.
You all sound like you’re trying to turn endocrinology into a New Age mantra. Calcitonin is barely relevant in adult humans. It’s a fetal hormone that’s been overhyped by people who think biology is poetry. Vitamin D? That’s the real player. Everything else is just noise dressed up as wisdom.
I just read this and felt really sad. Like, why does everything have to be so... competitive? Like vitamin D vs calcitonin? Why can't we just appreciate that our bodies are complex and we’re lucky to have any of it working at all?
You know what’s funny? In the 1980s, we were told calcium was the answer to everything, then it was vitamin D, now it’s this whole calcitonin ballet, and in 20 years it’ll be some new peptide from the gut-brain axis that’s ‘the real key’-and we’ll all forget calcitonin ever existed again. The truth is, the body doesn’t care about our labels. It just wants food, sun, sleep, and not being stressed out by people arguing about hormones on Reddit. You want bone health? Eat real food, go outside, move your body, and stop reading medical blogs written by people who’ve never held a bone in their hands. Also, I’ve lived in three countries and seen seven different medical systems-none of them agree on this stuff, so why are you so sure you’re right? Just saying.