Sarpagandha – What It Is and Why It Matters
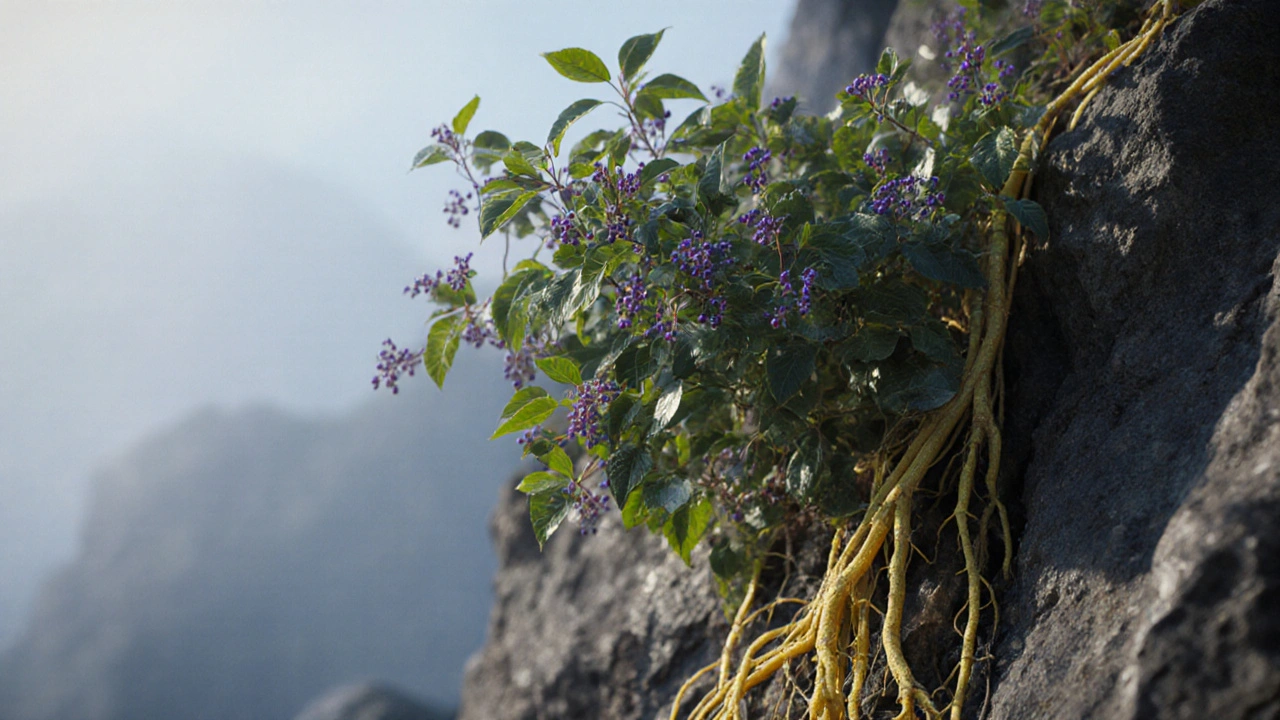
When working with Sarpagandha, a climbing shrub used for centuries to manage high blood pressure. Also known as Rauwolfia serpentina, it belongs to the same family as other medicinal plants that calm the nervous system.
Key compounds and health effects
The plant’s power comes from Reserpine, an alkaloid that blocks the storage of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine. By reducing norepinephrine release, reserpine lowers heart rate and relaxes blood vessels, directly tackling Hypertension, the leading risk factor for heart disease.
In Ayurveda, Sarpagandha is prized for its calming and blood‑pressure‑balancing properties. Practitioners often recommend a powdered root or a decoction taken before meals. Modern studies confirm that a daily dose of 0.5–1 g of the dried root can reduce systolic pressure by 10–15 mmHg in mild to moderate cases.
Compared with synthetic antihypertensives, Sarpagandha offers a gentler onset and fewer metabolic side effects. However, it still interacts with drugs that affect the central nervous system, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics. That’s why many of our articles discuss how natural remedies can complement or clash with prescription meds—topics you’ll see in the posts below.
Safety matters. Over‑use can lead to depression, nasal congestion, or a fainting spell due to excessive neurotransmitter depletion. Always start with the lowest effective dose, monitor blood pressure weekly, and consult a healthcare professional before mixing it with other medications.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive into related drugs, mental‑health management, and practical buying guides. Whether you’re looking for an affordable generic prescription or want to understand how herbal compounds like reserpine fit into modern therapy, the collection gives you clear, actionable information.