Eplerenone and Osteoporosis: What You Need to Know
Eplerenone helps manage heart failure and high blood pressure, but long-term use may increase osteoporosis risk. Learn who’s at risk and how to protect your bones while staying on this medication.
When you hear eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure after a heart attack. Also known as a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, it works by stopping excess aldosterone from making your body hold onto salt and water—something that can strain your heart and raise your blood pressure. Unlike older drugs that hit multiple hormone receptors, eplerenone is pickier. That means fewer side effects like sexual dysfunction or breast tenderness, which you often see with spironolactone, its older cousin.
It’s not a first-line drug for everyone, but it shines in specific cases. If you’ve had a heart attack and your heart isn’t pumping well, doctors often add eplerenone to your regimen—especially if you’re already on ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers. Studies show it cuts the risk of death and hospital stays in these patients. It’s also used when other diuretics aren’t enough, or when you can’t tolerate them. But it’s not for everyone. If your kidneys aren’t working well or your potassium levels are already high, your doctor will skip it. That’s because eplerenone can make potassium climb dangerously, leading to heart rhythm problems.
People often ask how it stacks up against other meds. Spironolactone does a similar job but with more side effects. Losartan and lisinopril work differently—they block angiotensin, not aldosterone. Sometimes they’re used together. If you’re on eplerenone, you’ll need regular blood tests to check potassium and kidney function. It’s not a quick fix, but over time, it helps your heart recover and reduces fluid buildup without the muscle cramps or dizziness you get from stronger diuretics.
What you’ll find in the posts below are real comparisons: how eplerenone fits with other heart meds, what patients actually experience, and when switching to something else makes sense. You’ll see how it plays with blood pressure drugs, what foods to avoid, and why some people do better on it than others. No fluff. Just clear, practical info from people who’ve been there.
Eplerenone helps manage heart failure and high blood pressure, but long-term use may increase osteoporosis risk. Learn who’s at risk and how to protect your bones while staying on this medication.

As a blogger, I've recently been researching the use of calcium carbonate in the cosmetic industry. I've discovered that it offers some great benefits, such as acting as a gentle exfoliant and helping to balance the pH levels of our skin. However, there are also some concerns surrounding its use, including potential irritation for those with sensitive skin and the possibility of environmental harm caused by mining for this ingredient. Overall, it's important to weigh the pros and cons and consider personal skin needs when choosing products containing calcium carbonate. Stay tuned for a more in-depth look at this intriguing ingredient in an upcoming post!
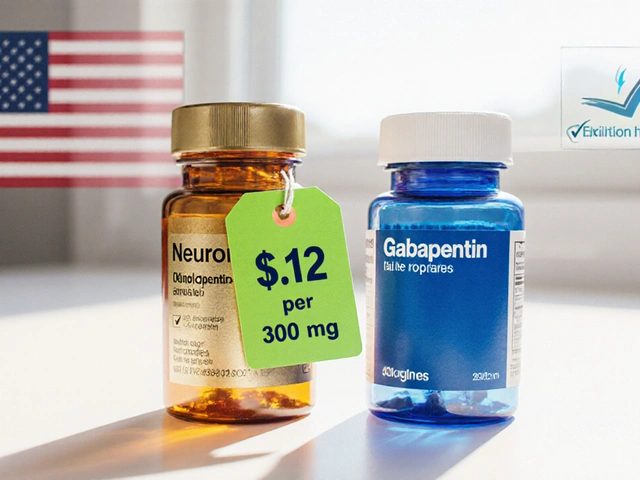
Learn how to safely buy cheap generic Neurontin online, compare reputable pharmacies, spot scams, and save money while staying compliant.

A practical guide to safely buying cheap generic lisinopril online in Australia, covering legal checks, pharmacy verification, price comparisons, ordering steps and fraud avoidance.

Menstrual cramps can be quite a challenge for many of us, so I've put together a self-care routine to help alleviate the pain. First, try incorporating some light exercise, like yoga or stretching, to release endorphins and relieve cramps. Second, applying heat through a heating pad or warm bath can provide comfort and soothe muscles. It's also essential to maintain a balanced diet and stay hydrated during our periods. Lastly, don't forget to prioritize rest and relaxation to help manage stress and reduce cramps.

Colchicine and macrolides like clarithromycin can cause life-threatening toxicity due to combined CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibition. Azithromycin is the only safe macrolide option. Know the risks and how to avoid them.
